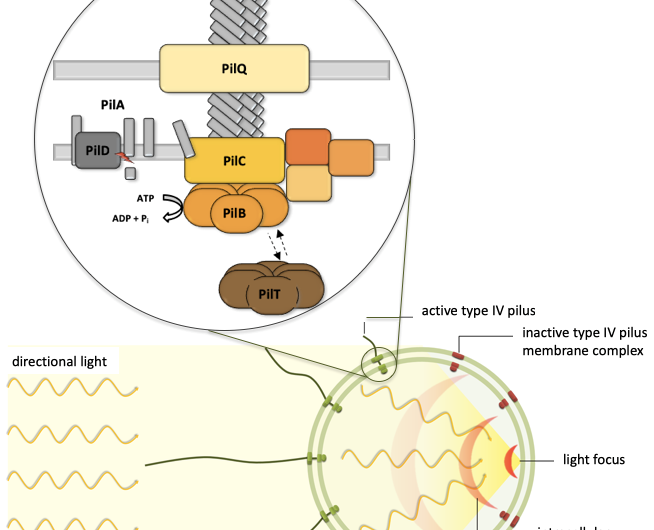
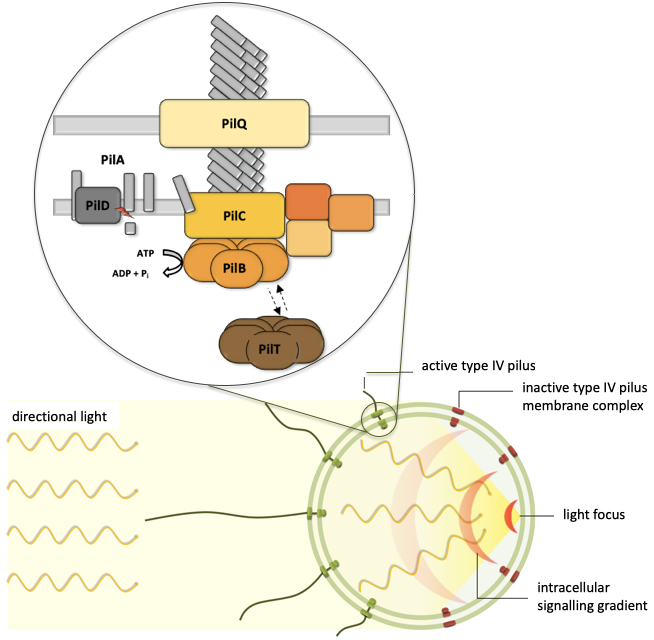
Bacterial movement using type IV pili relies on dynamic, polar assembly of the motility machinery in order to move into a certain direction. In cyanobacterial phototaxis, localized control of pilus activity by light gives us a unique opportunity to probe the assembly dynamics of this molecular machine.
In the first funding period, we identified and studied differences in the composition, the function, and the regulation of the cyanobacterial type IV pilus complex which are based on the light dependency of phototactic motility. These analyses involved the identification of cyanobacterial membrane complexes using a complexome study, the functional analysis of cyanobacteria-specific pilus subunits, and the life cell imaging of pili using advanced microscopic techniques. Based on these studies, we will further explore the light-dependent dynamics of type IV pilus complexes and the modulation of different pilus functions by the assembly of distinct subcomplexes.
Funding:
SFB 1381 Dynamic Organization of Cellular Protein Machineries: From Biogenesis and Modular Assembly to Function
Key Publications:
Nakane D, Enomoto G, Bähre H, Hirose Y, Wilde A, Nishizaka T (2022) Thermosynechococcus switches the direction of phototaxis by a c-di-GMP dependent process with high spatial resolution, eLife 11: e73405.
Han Y, Jakob A, Engel S, Wilde A, Schuergers N (2022) PATAN-domain regulators interact with the Type IV pilus motor to control phototactic orientation in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis. Mol. Microbiol. 117: 790-801.
Oeser S, Wallner T, Schuergers N, Bučinská L, Sivabalasarma S, Bähre H, Albers SV, Wilde A (2021) Minor pilins are involved in motility and natural competence of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Mol. Microbiol. 116: 743-765.
Wallner T, Pedroza L, Voigt K, Kaever V, Wilde A (2020) The cyanobacterial phytochrome 2 regulates the expression of motility-related genes through the second messenger cyclic di-GMP. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci.19: 631-643.
Conradi FD, Zhou RQ, Oeser S, Schuergers N, Wilde A, Mullineaux CW (2019) Factors controlling floc formation and structure in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. Strain PCC 6803. J. Bacteriol. 201:e00344-19.
Jakob A, Nakamura H, Kobayashi A, Sugimoto Y, Wilde A, Masuda S. (2019) The (PATAN)-CheY-like response regulator PixE interacts with the motor ATPase PilB1 to control negative phototaxis in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Plant Cell Physiol. 61, 296-307.
Wilde A, Mullineaux CW. (2017) Light-controlled motility in prokaryotes and the problem of directional light perception. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 41, 900-922.
Schuergers N, Mullineaux CW, Wilde A. (2017) Cyanobacteria in motion. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 37, 109-115.
Angerer V, Schwenk P, Wallner T, Kaever V, Hiltbrunner A, Wilde A. (2017) The protein Slr1143 is an active diguanylate cyclase in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 and interacts with the photoreceptor Cph2. Microbiology 163, 920-930.
Schuergers N, Lenn T, Kampmann R, Meissner MV, Esteves T, Temerinac-Ott M, Korvink JG, Lowe AR, Mullineaux CW, Wilde A. (2016) Cyanobacteria use micro-optics to sense light direction. eLife 5, e12620.
SchuergersN, NürnbergDJ, WallnerT, MullineauxCW, WildeA. (2015) PilB localisation correlates with the direction of twitching motility in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Microbiology 161, 960-966
Schuergers N, Wilde A. (2015) Appendages of the cyanobacterial cell. Life 5, 700-715.
Savakis P, De Causmaecker S, Angerer V, Ruppert U, Anders K, Essen LO, Wilde A. (2012) Light-induced alteration of c-di-GMP level controls motility of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Mol. Microbiol. 85, 239-251.
Wilde, A., Fiedler, B., Börner, T. (2002) The cyanobacterial phytochrome Cph2 inhibits phototaxis towards blue light. Mol. Microbiol. 44, 981-988.
